Scientific Hand Charts Collection:
Wlliams-Beuren syndrome [WS/WSB]
1 Hand Chart for Williams syndrome!
Williams syndrome (WS), a.k.a. Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a rare neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by: an "elfin" facial appearance, an unusually cheerful demeanor & ease with strangers, combined with developmental delay featured with strong language skills; cardiovascular problems are also typical.
Prevalence: Present roughly one in 14,000 births.
One hand charts is available for Kabuki syndrome describing the significance of various typical dermatoglyphics, often combined with a Sydney line - see picture below.
NOTICE: Individual hand features described below should not get associated in isolation with any theme; only combinations involving multiple hand levels have potential for diagnostic purposes.
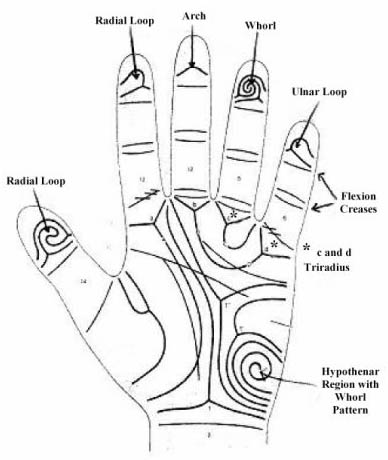
QUOTE: '"Phantom picture" of Williams-Beurend syndrome. 1 = frequent whorls on all fingertips; 2 = radial loops on 3rd and/or 4th finger; 3 = absence of the c triradius (C-0); 4 = A line terminations in 5/5'/5"; 5 = D line terminations in 11; 6 = frequent distal axial triradius t"; 7 = very frequent Sydney line; 8 = ulnarly displaced t triradius; 9 = papillary ridge dysplasia and/or hypoplasia.
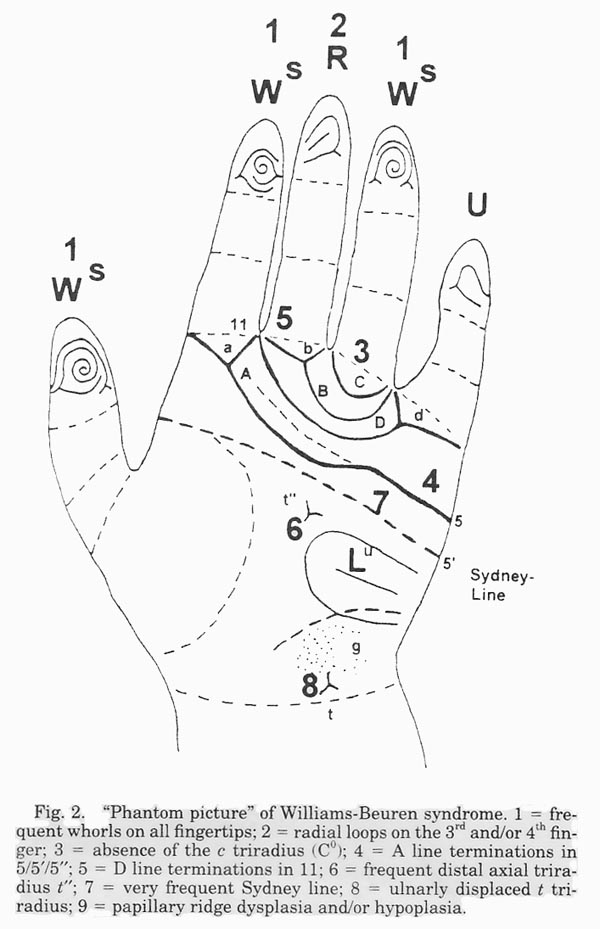
Dermatoglyphic Pecularities in Patients With Williams-Beuren syndrome;
Am J Med Genet, 1994 Nov; 31(3) - 53: p.233; authors: A. Rodewald, et al.
Other significant hand signs (not reported inside the hand charts):
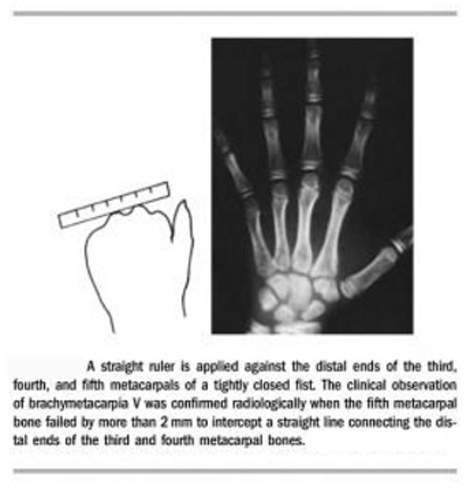
A short 5th metacarpal bone (50%) has been observed in about half of Williams syndrome patients - see picture below; a short 4th metacarpal bone (40%) is also very common (source: I. Borg et al., 2015).
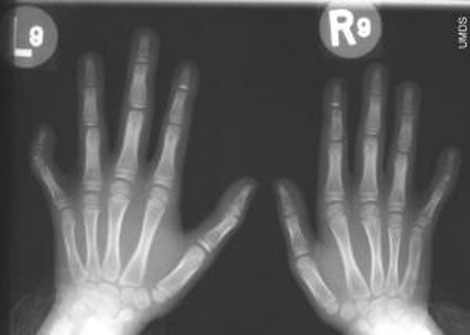
Clinodactyly of the 5th finger (50%) is also seen in about half of William syndrome patients - see picture below; clinodactyly of the 4th finger (10%) may be present as well (source: I. Borg et al., 2015).
Some individuals with Williams syndrome display stereotyped behaviours such as hand flapping. Also, about 90% of children with WS are hypersensitive to particular sounds that would not cause discomfort in most people; the noises may be very distressing to the WS children, who will typically put their hands over their ears. (Source: Canadian Association for Williams Syndrome)
Short nails is also recognized to represent a common feature inside the pediatric age group involving Williams syndrome. (Source: Neurorehabilitation for the Physical Therapist Assistant, p.106)
All significant hand signs listed above for Williams syndrome together cover six out of the nine perspectives of the hand as defined according Multi-Perspective Hand Reading (including hand level 1, 4, 5, 7, 8 & 9).
A summary of the most significant hand sign combinations in Williams syndrome is described here:
Decoding the language of the hand:
hand sign combinations in Williams syndrome!
Hand charts are available for many other diagnostic issues;
start browsing HERE
![]() SCIENTIFIC HAND CHARTS: Introduction
SCIENTIFIC HAND CHARTS: Introduction
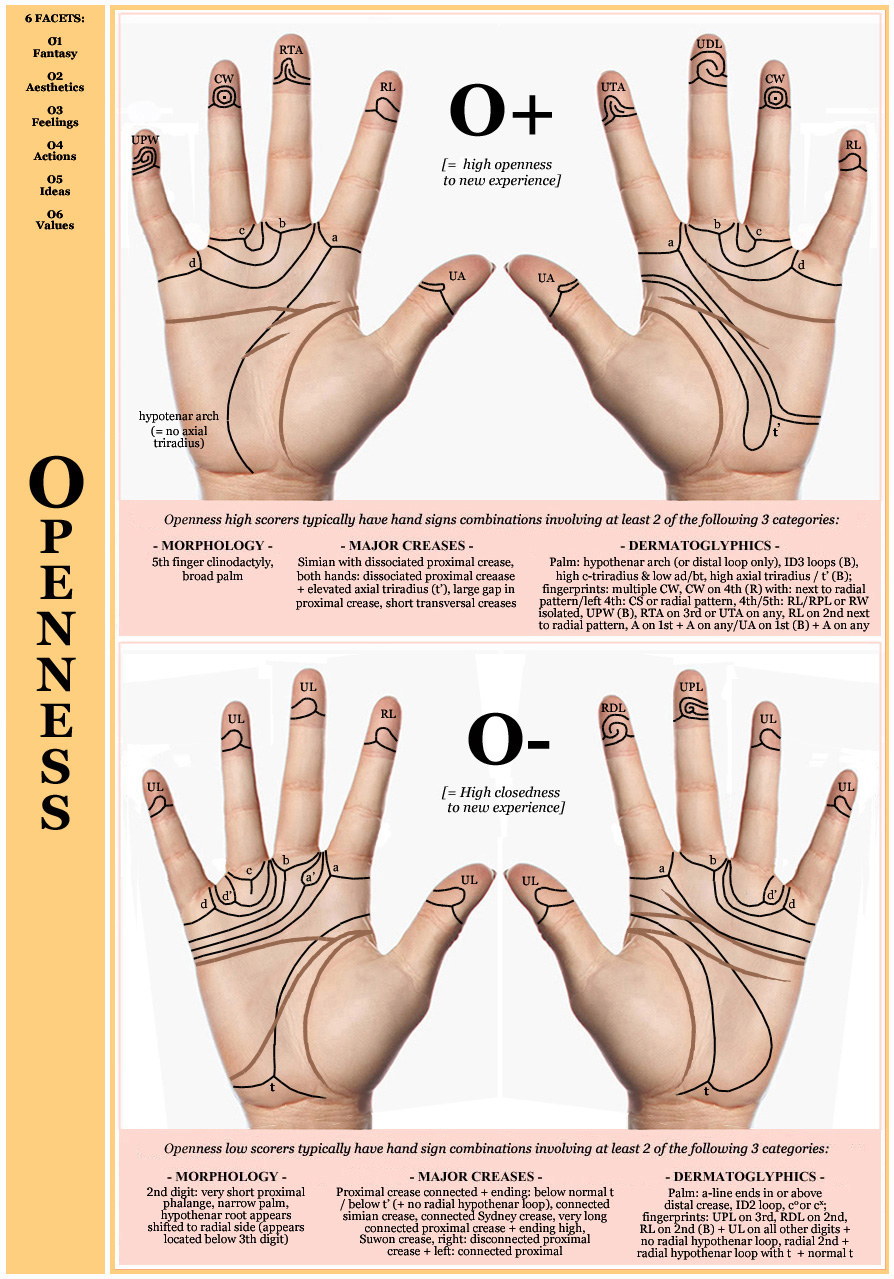
Hand charts for Big Five personality dimensions:
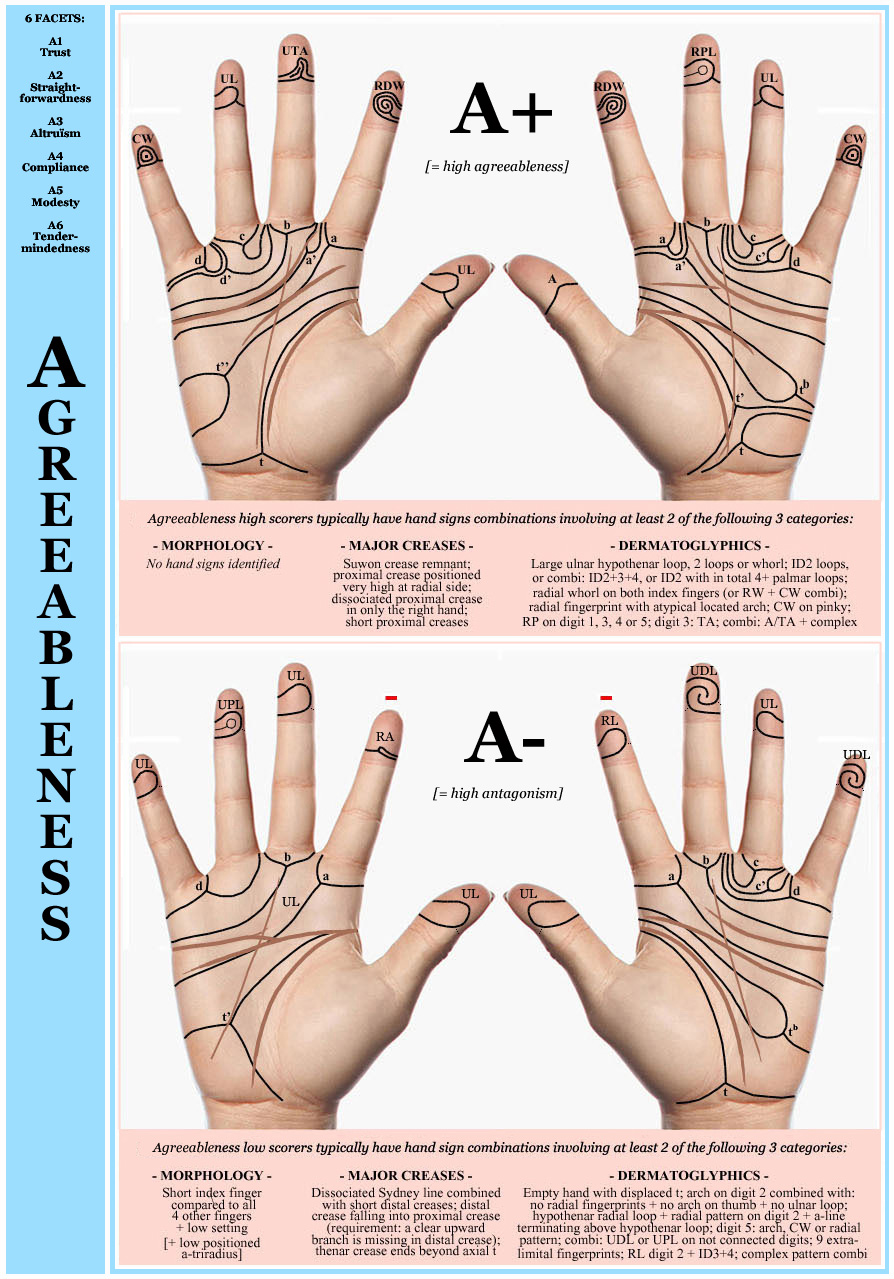
• Hand chart(s) for Agreeableness (2x: 1 in 4 people)
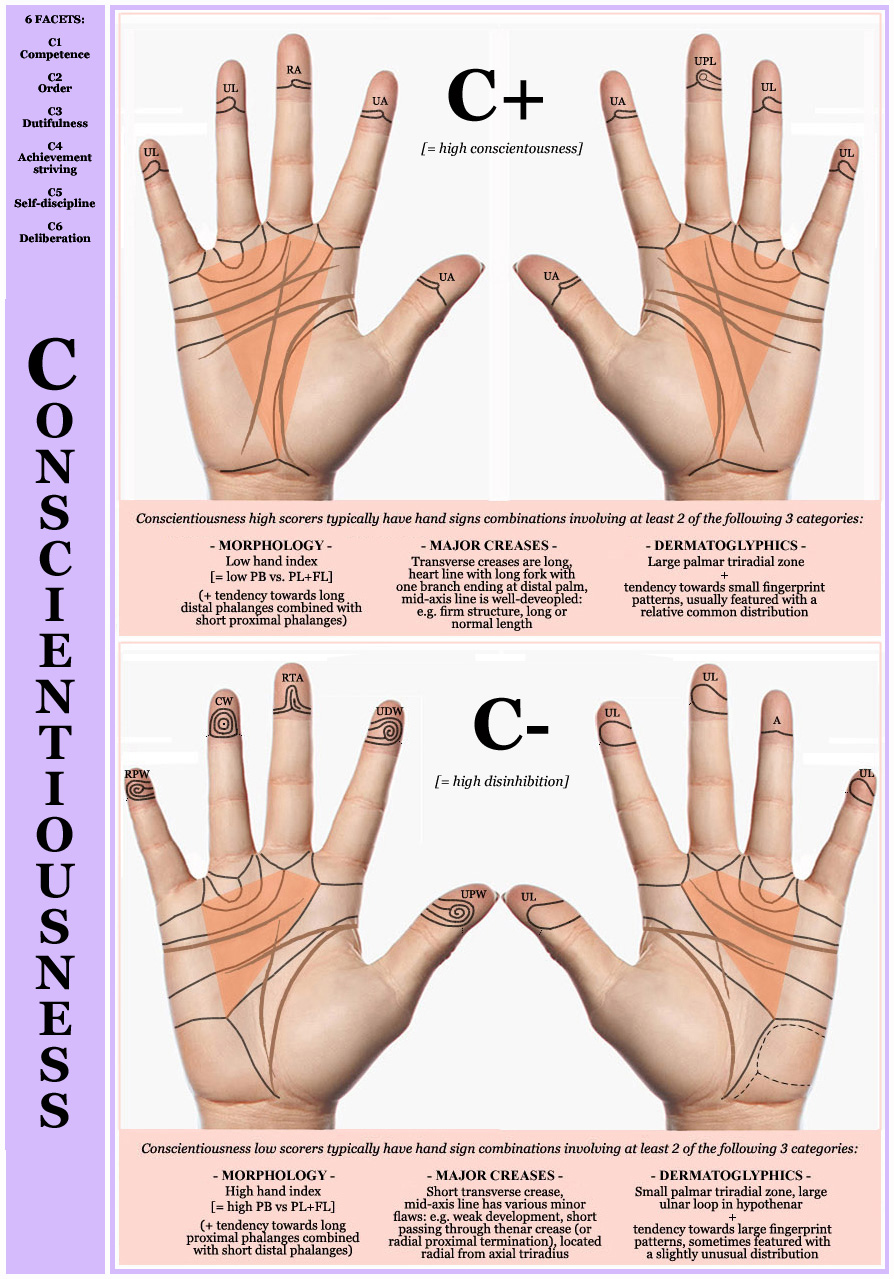
• Hand chart(s) for Conscientiousness (2x: 1 in 4 people)
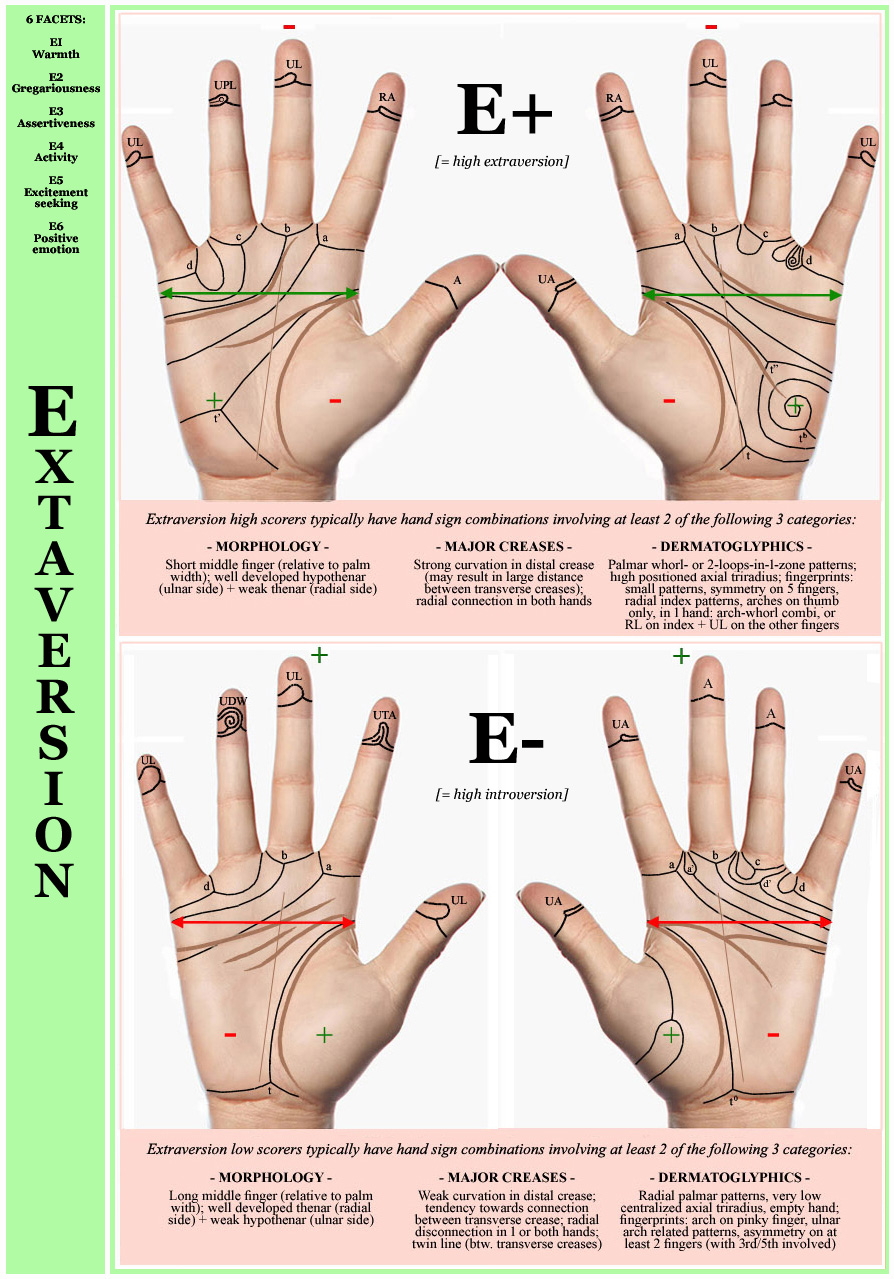
• Hand chart(s) for Extraversion (2x: 1 in 4 people)
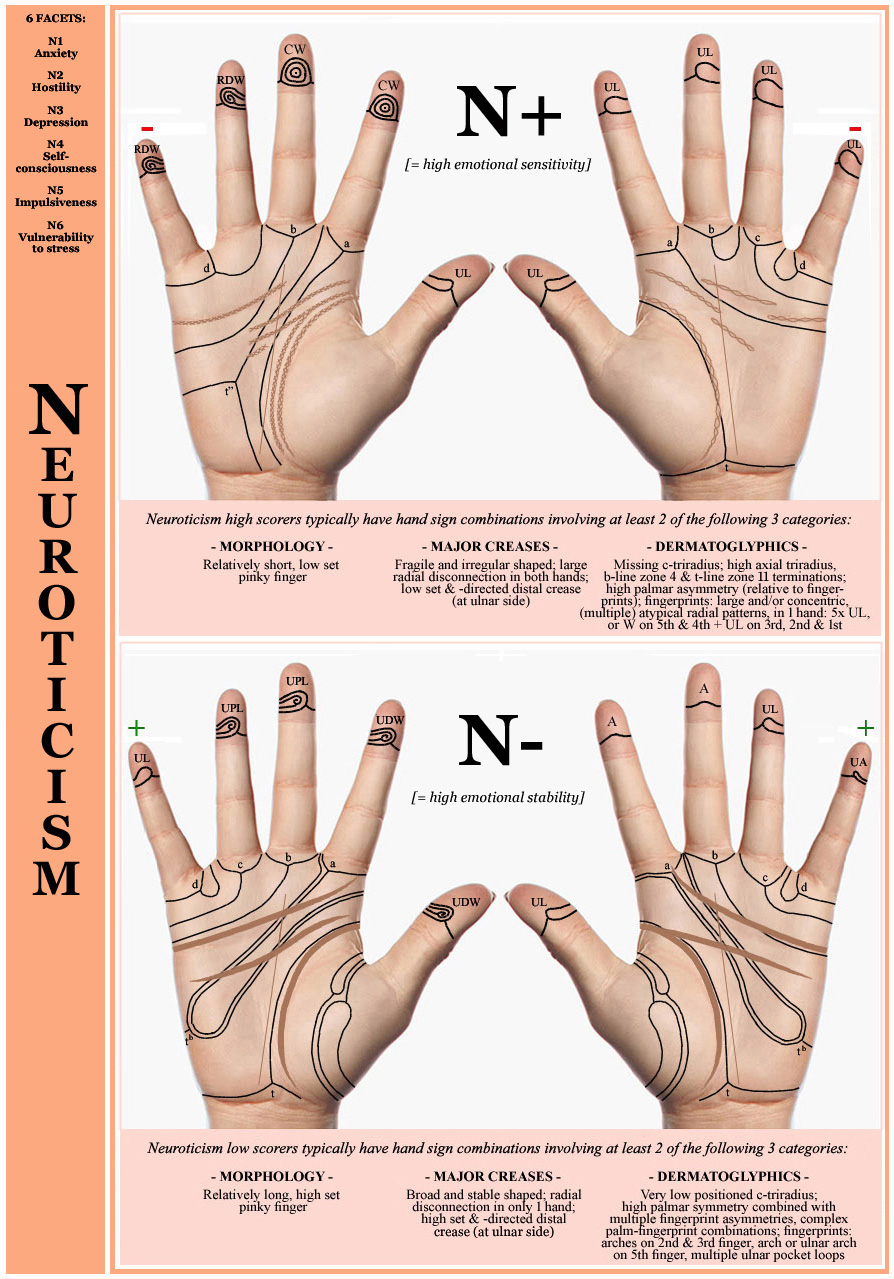
• Hand chart(s) Neuroticism (2x: 1 in 4 people)
• Hand chart(s) Openness (2x: 1 in 4 people)
Hand charts for diseases:
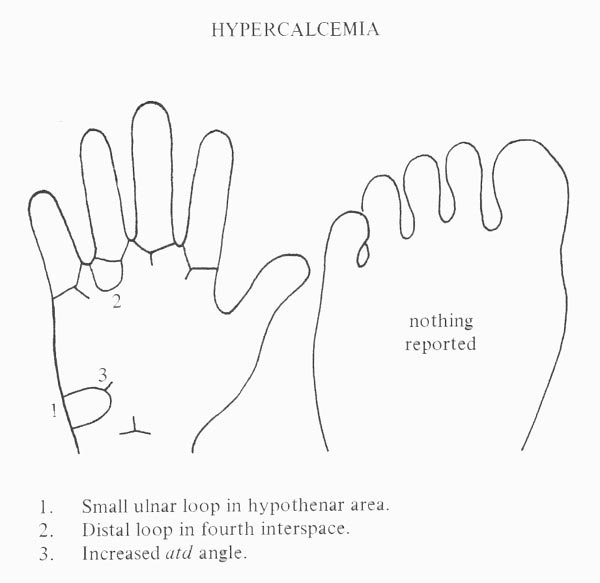
• Hand charts for hypercalcemia (1 in 4,000 people)
Hand charts for syndromes:
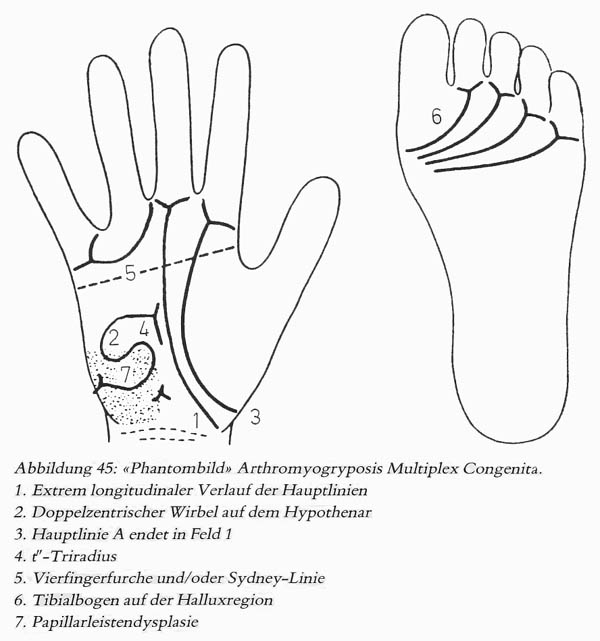
• Hand charts for arthrogryposis (1 in 10,000 people)
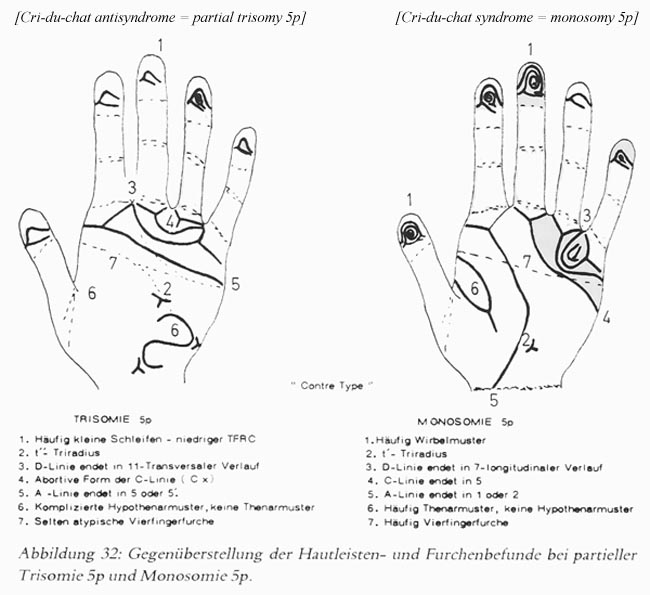
• Hand charts for cri-du-chat syndrome (1 in 30,000 people)
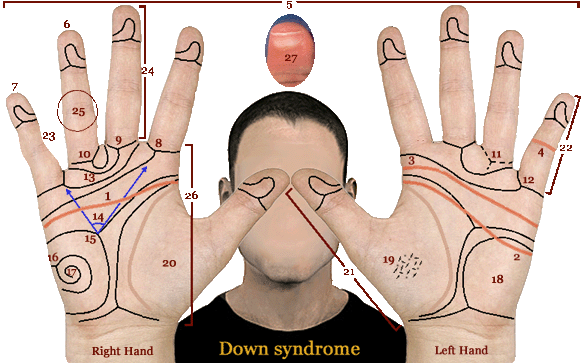
• Hand charts for Down syndrome (1 in 700 live births)
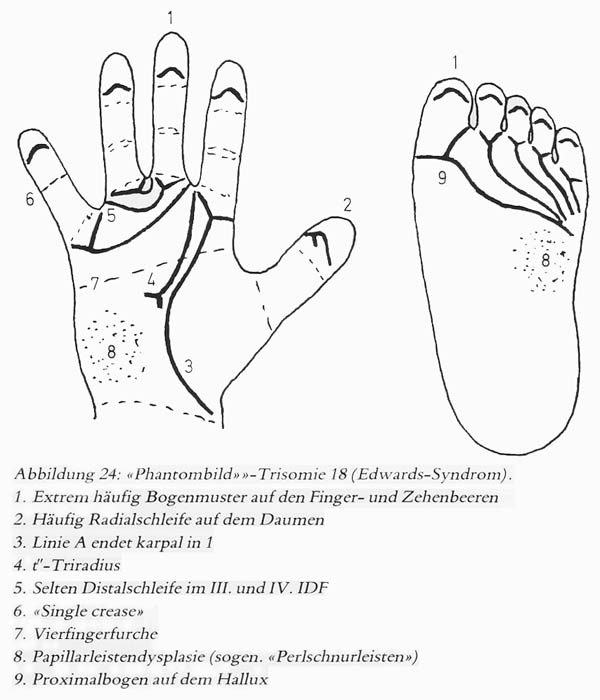
• Hand charts for Edwards syndrome (1 in 6,000 live births)
• Hand charts for fetal alcolhol syndrome (1 in 500 people)
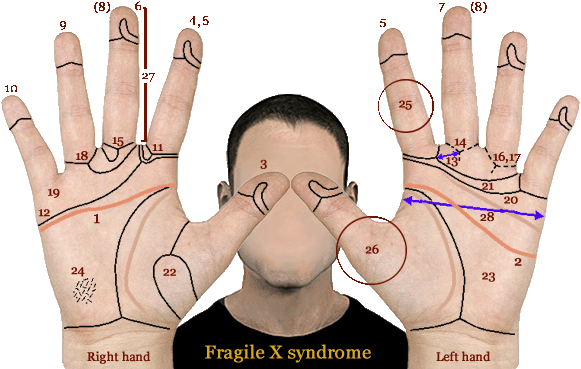
• Hand charts for fragile-X syndrome (1 in 5,000 people)
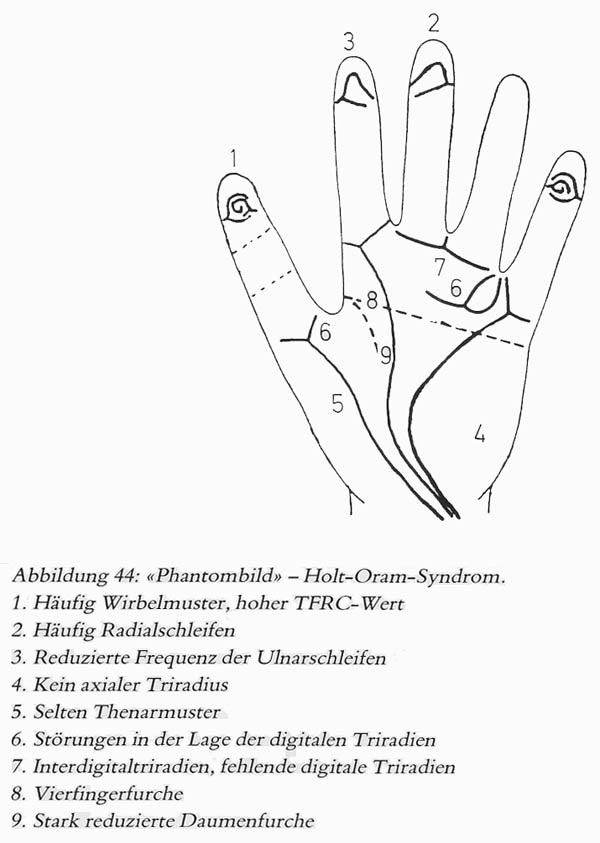
• Hand charts for Holt-Oram syndrome (1 in 100,000 live b.)
• Hand charts for Kabuki syndrome (1 in 32,000 people)
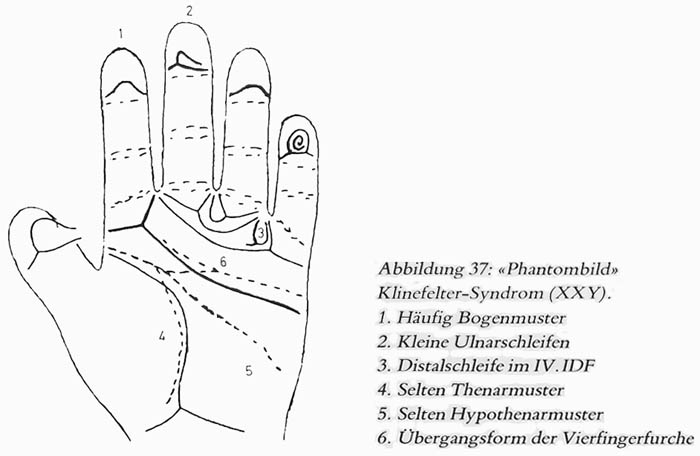
• Hand charts for Klinefelter syndrome (1 in 1000 males)
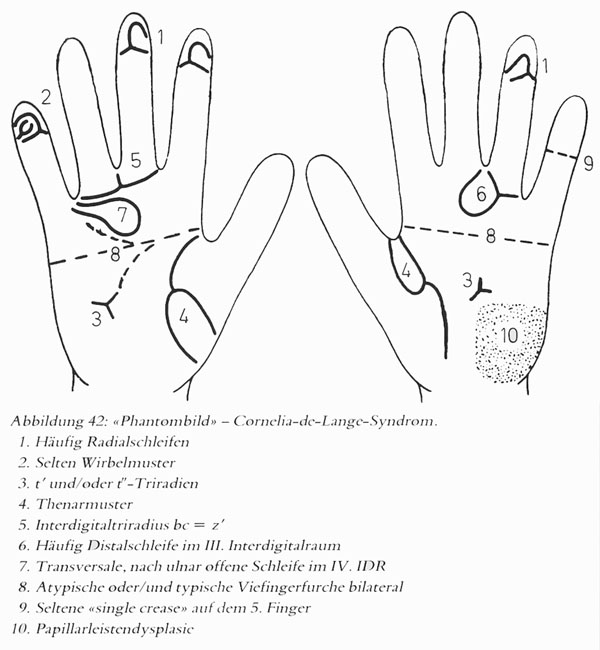
• Hand charts for de Lange syndrome (1 in 15,000 live births)
• Hand charts for Marfan syndrome (1 in 5,000 people)
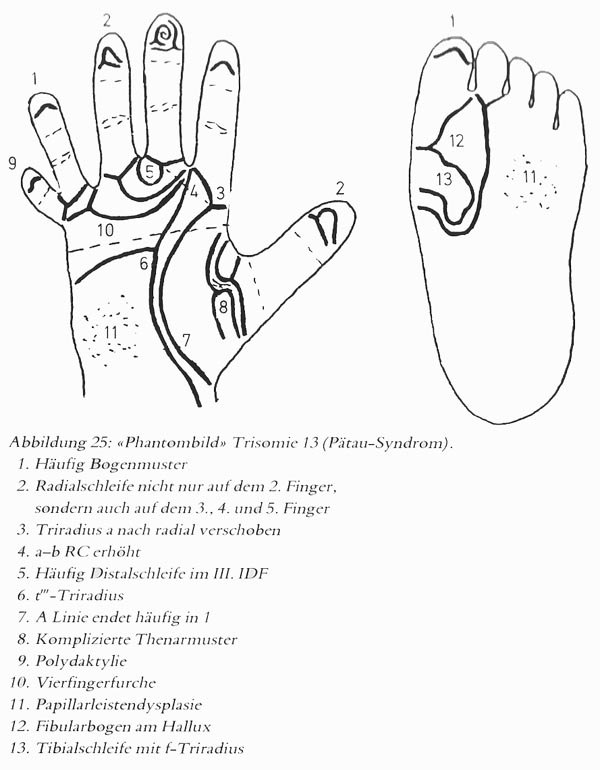
• Hand charts for Patau syndrome (1 in 15,000 live births)
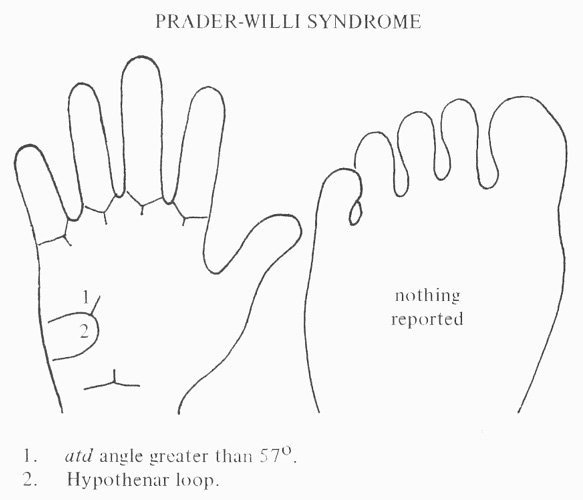
• Hand charts for Prader-Willi syndrome (1 in 15,000 births)
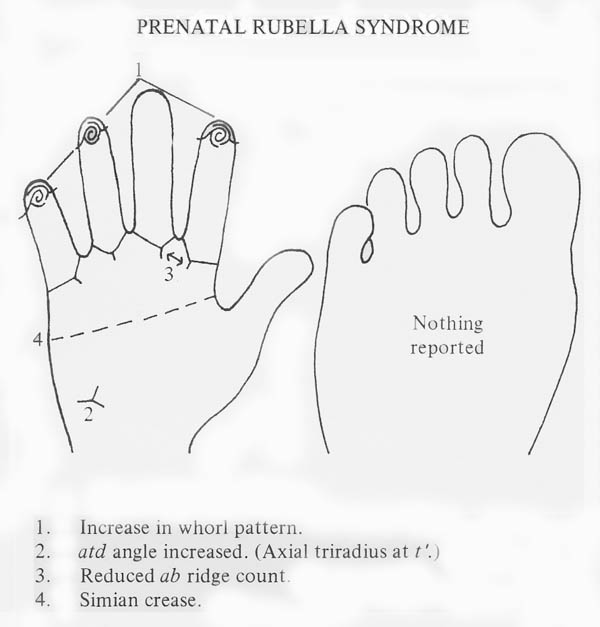
• Hand charts for Rubella syndrome (1 in 100,000 people)
• Hand charts for Rubinstein syndrome (1 in 200,000 births)
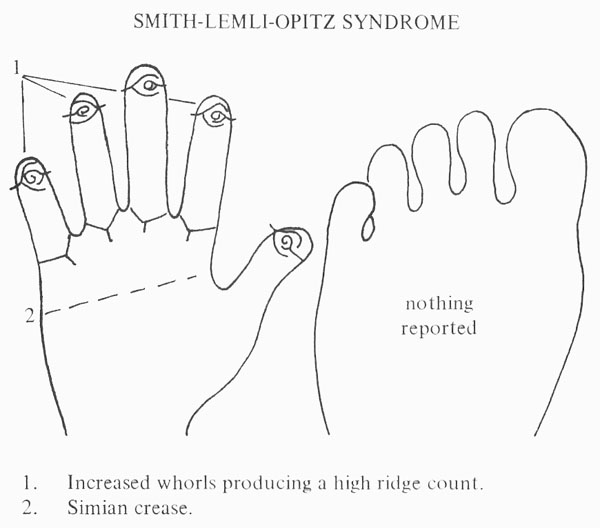
• Hand charts for SLOS (1 in 40,000 births)
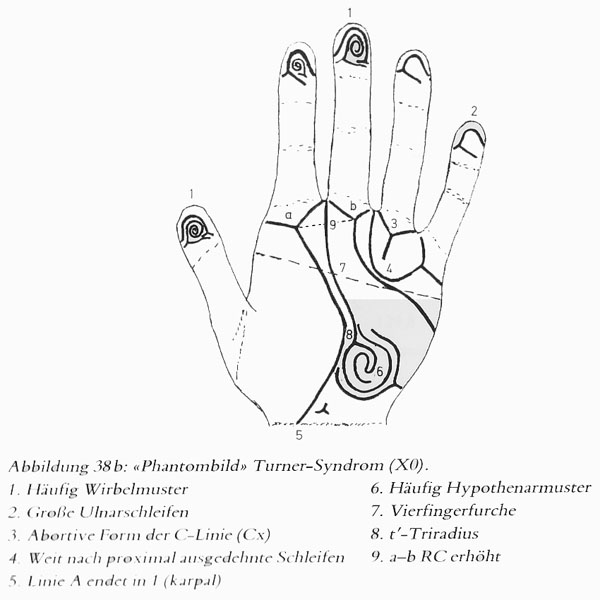
• Hand charts for Turner syndrome (1 in 2,000 female births)
• Hand charts for Warkany syndrome (1 in 200,000 births)
• Hand charts for Williams syndrome (1 in 14,000 births)
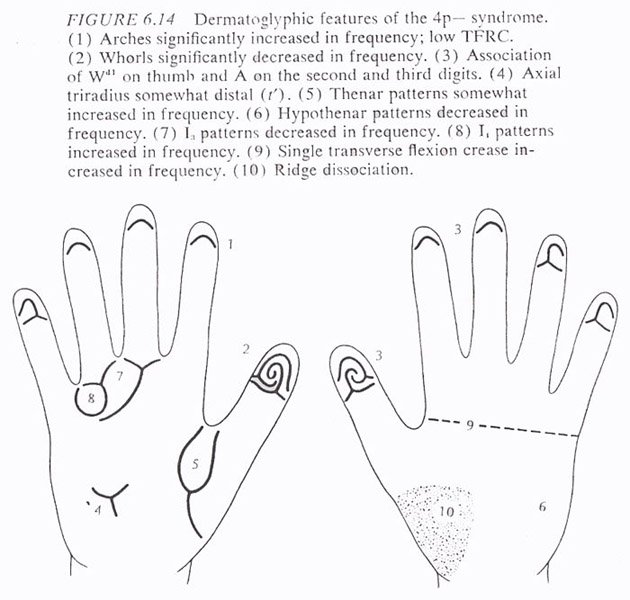
• Hand charts for Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (1 in 50,000 b.)
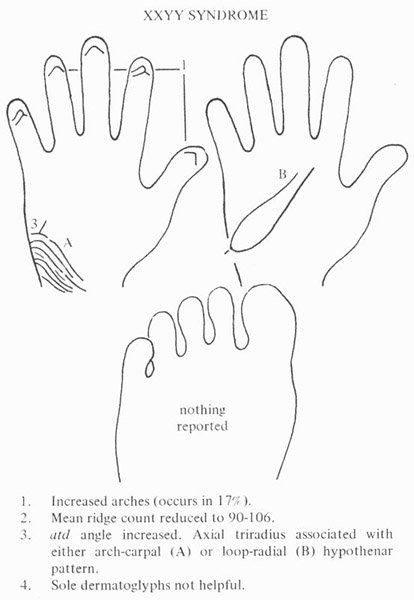
• Hand charts for XXYY syndrome (1 in 30,000 male births)
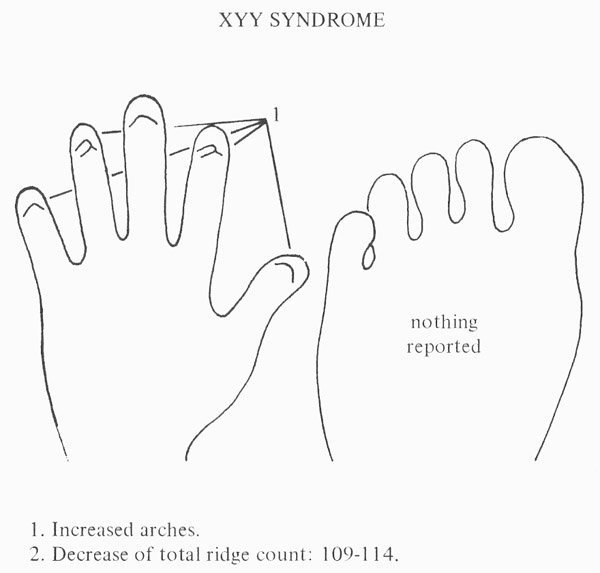
• Hand charts for XYY syndrome (1 in 1,000 male births)
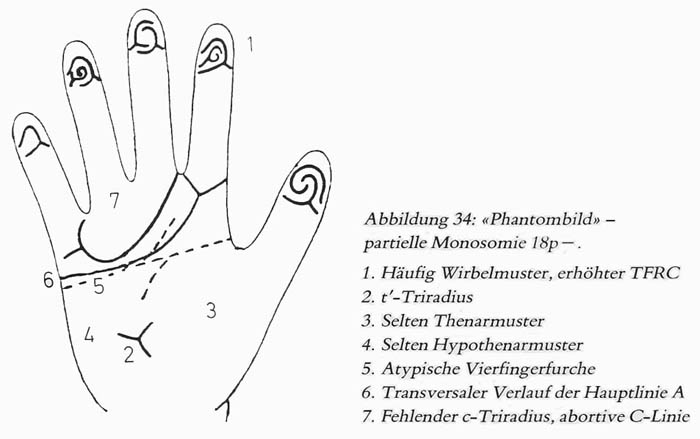
• Hand charts for 18 deletion syndromes (2 in 40,000 live b.)
NOTICE: Reflexology hand charts are not included in this section because the scientific foundation of any of such charts is actually unknown; nevertheless, you can read more about the fundamentals of such charts HERE.
Other charts & maps:
• Fingerprints world map
• Hand reading experts world map
• Hand reflexology charts